ציוד נדרש
כרטיס פיתוח Arduino.מגן Ethernet
חיישן לחץ ברומטרי SCP1000
מעגל
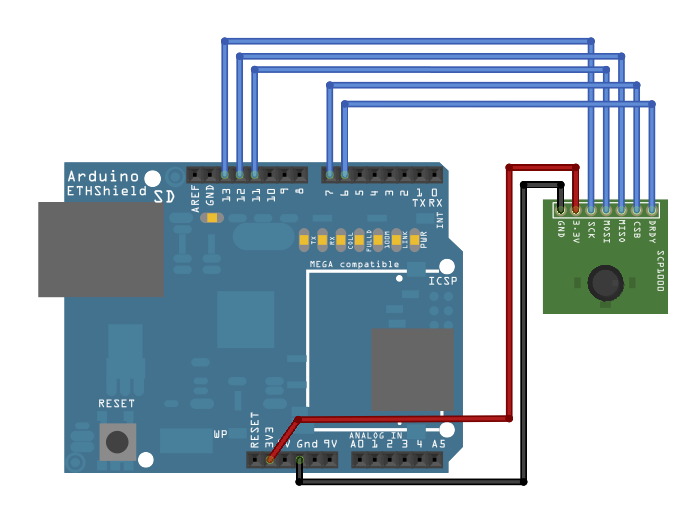
החיישן יהיה מחובר לקווים 6,7 ו-11-13 של כרטיס ה-Arduino ויקבל את המתח מקו ה-3.3V. חברו את קו ה-DRDY של החיישן לקו 6 של הארדואינו ואת קו ה-CSB לקו 7 של הבקר. קו ה-MOSI צריך להיות מחובר לקו 11 של הבקר וקו ה-MISO לקו 12. לבסוף, חברו את קו ה-SCK לקו 13 של הארדואינו וודאו שהחיישן והבקר משתפים את האדמה (GND).אחרי חיבור החיישן, מגן ה-Ethernet צריך להיות מחובר לרשת עם כבל Ethernet. תצטרכו לשנות את הגדרות הרשת בתוכנה כדי להתאים אותם לרשת שלכם.
החיבורים בתמונה הבאה מוצגים על מגן ה-Ethernet שמורכב על כרטיס הארדואינו.
שרטוט
אין צורך בשרטוט לדוגמה זו.קוד
- קוד: בחר הכל
/*
SCP1000 Barometric Pressure Sensor Display
Serves the output of a Barometric Pressure Sensor as a web page.
Uses the SPI library. For details on the sensor, see:
http://www.sparkfun.com/commerce/product_info.php?products_id=8161
This sketch adapted from Nathan Seidle's SCP1000 example for PIC:
http://www.sparkfun.com/datasheets/Sensors/SCP1000-Testing.zip
Circuit:
SCP1000 sensor attached to pins 6,7, and 11 - 13:
DRDY: pin 6
CSB: pin 7
MOSI: pin 11
MISO: pin 12
SCK: pin 13
created 31 July 2010
by Tom Igoe
*/
#include <Ethernet.h>
// the sensor communicates using SPI, so include the library:
#include <SPI.h>
// assign a MAC address for the Ethernet controller.
// fill in your address here:
byte mac[] = {
0xDE, 0xAD, 0xBE, 0xEF, 0xFE, 0xED
};
// assign an IP address for the controller:
IPAddress ip(192, 168, 1, 20);
// Initialize the Ethernet server library
// with the IP address and port you want to use
// (port 80 is default for HTTP):
EthernetServer server(80);
//Sensor's memory register addresses:
const int PRESSURE = 0x1F; //3 most significant bits of pressure
const int PRESSURE_LSB = 0x20; //16 least significant bits of pressure
const int TEMPERATURE = 0x21; //16 bit temperature reading
// pins used for the connection with the sensor
// the others you need are controlled by the SPI library):
const int dataReadyPin = 6;
const int chipSelectPin = 7;
float temperature = 0.0;
long pressure = 0;
long lastReadingTime = 0;
void setup() {
// start the SPI library:
SPI.begin();
// start the Ethernet connection and the server:
Ethernet.begin(mac, ip);
server.begin();
// initalize the data ready and chip select pins:
pinMode(dataReadyPin, INPUT);
pinMode(chipSelectPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
//Configure SCP1000 for low noise configuration:
writeRegister(0x02, 0x2D);
writeRegister(0x01, 0x03);
writeRegister(0x03, 0x02);
// give the sensor and Ethernet shield time to set up:
delay(1000);
//Set the sensor to high resolution mode tp start readings:
writeRegister(0x03, 0x0A);
}
void loop() {
// check for a reading no more than once a second.
if (millis() - lastReadingTime > 1000) {
// if there's a reading ready, read it:
// don't do anything until the data ready pin is high:
if (digitalRead(dataReadyPin) == HIGH) {
getData();
// timestamp the last time you got a reading:
lastReadingTime = millis();
}
}
// listen for incoming Ethernet connections:
listenForEthernetClients();
}
void getData() {
Serial.println("Getting reading");
//Read the temperature data
int tempData = readRegister(0x21, 2);
// convert the temperature to celsius and display it:
temperature = (float)tempData / 20.0;
//Read the pressure data highest 3 bits:
byte pressureDataHigh = readRegister(0x1F, 1);
pressureDataHigh &= 0b00000111; //you only needs bits 2 to 0
//Read the pressure data lower 16 bits:
unsigned int pressureDataLow = readRegister(0x20, 2);
//combine the two parts into one 19-bit number:
pressure = ((pressureDataHigh << 16) | pressureDataLow) / 4;
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temperature);
Serial.println(" degrees C");
Serial.print("Pressure: " + String(pressure));
Serial.println(" Pa");
}
void listenForEthernetClients() {
// listen for incoming clients
EthernetClient client = server.available();
if (client) {
Serial.println("Got a client");
// an http request ends with a blank line
boolean currentLineIsBlank = true;
while (client.connected()) {
if (client.available()) {
char c = client.read();
// if you've gotten to the end of the line (received a newline
// character) and the line is blank, the http request has ended,
// so you can send a reply
if (c == '\n' && currentLineIsBlank) {
// send a standard http response header
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-Type: text/html");
client.println();
// print the current readings, in HTML format:
client.print("Temperature: ");
client.print(temperature);
client.print(" degrees C");
client.println("<br />");
client.print("Pressure: " + String(pressure));
client.print(" Pa");
client.println("<br />");
break;
}
if (c == '\n') {
// you're starting a new line
currentLineIsBlank = true;
} else if (c != '\r') {
// you've gotten a character on the current line
currentLineIsBlank = false;
}
}
}
// give the web browser time to receive the data
delay(1);
// close the connection:
client.stop();
}
}
//Send a write command to SCP1000
void writeRegister(byte registerName, byte registerValue) {
// SCP1000 expects the register name in the upper 6 bits
// of the byte:
registerName <<= 2;
// command (read or write) goes in the lower two bits:
registerName |= 0b00000010; //Write command
// take the chip select low to select the device:
digitalWrite(chipSelectPin, LOW);
SPI.transfer(registerName); //Send register location
SPI.transfer(registerValue); //Send value to record into register
// take the chip select high to de-select:
digitalWrite(chipSelectPin, HIGH);
}
//Read register from the SCP1000:
unsigned int readRegister(byte registerName, int numBytes) {
byte inByte = 0; // incoming from the SPI read
unsigned int result = 0; // result to return
// SCP1000 expects the register name in the upper 6 bits
// of the byte:
registerName <<= 2;
// command (read or write) goes in the lower two bits:
registerName &= 0b11111100; //Read command
// take the chip select low to select the device:
digitalWrite(chipSelectPin, LOW);
// send the device the register you want to read:
int command = SPI.transfer(registerName);
// send a value of 0 to read the first byte returned:
inByte = SPI.transfer(0x00);
result = inByte;
// if there's more than one byte returned,
// shift the first byte then get the second byte:
if (numBytes > 1) {
result = inByte << 8;
inByte = SPI.transfer(0x00);
result = result | inByte;
}
// take the chip select high to de-select:
digitalWrite(chipSelectPin, HIGH);
// return the result:
return (result);
}
ראו גם:
מדריך לתחילת העבודה עם מגן Ethernet (אנגלית) - TODOספריית Ethernet
ChatServer - יצירת שרת צ'ט פשוט
AdvancedChatServer - שרת שמעביר את הנתונים לכל הלקוחות המחוברים חוץ מזה ששולח אותם
WebClient - שולח בקשות HTTP
WebClientRepeating - חוזר על שליחת בקשות HTTP
WebServer - שרת WEB פשוט שמציג עמוד HTML עם ערך של חיישן אנלוגי
UDPSendReceiveString - קבלה ומשלוח הודעות טקסט דרך UDP
UdpNtpClient - קבלת זמן משרת NTP (שרת Network Time Protocol)
DnsWebClient - צד ב-Client שמבוסס על DHCP ו-DNS
DhcpChatServer - שרת צ'ט פשוט שמבוסס על DHCP
DhcpAddressPrinter - מקבל כתובת דרך DHCP ומדפיס אותה
TelnetClient - צד ה-Client פשוט לחיבור ל-Telnet
פירוט שפת תכנות לסביבת Arduino
עמוד זה הוא תרגום של Barometric Pressure Web Server לפי רישיון Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0.